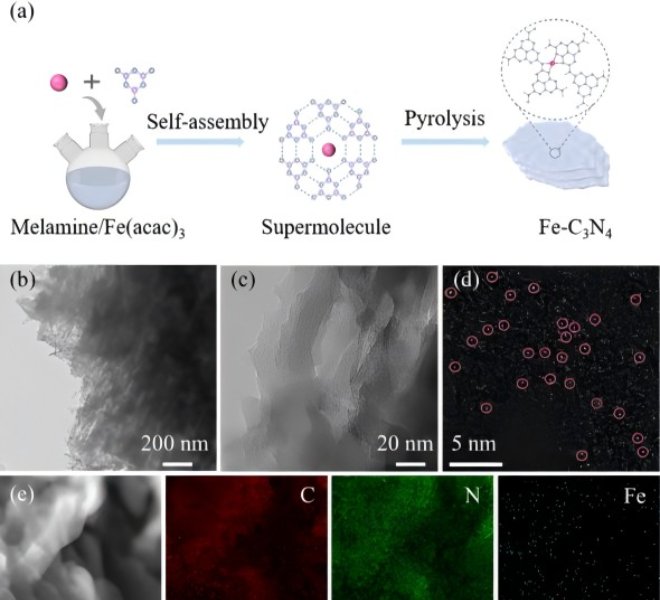
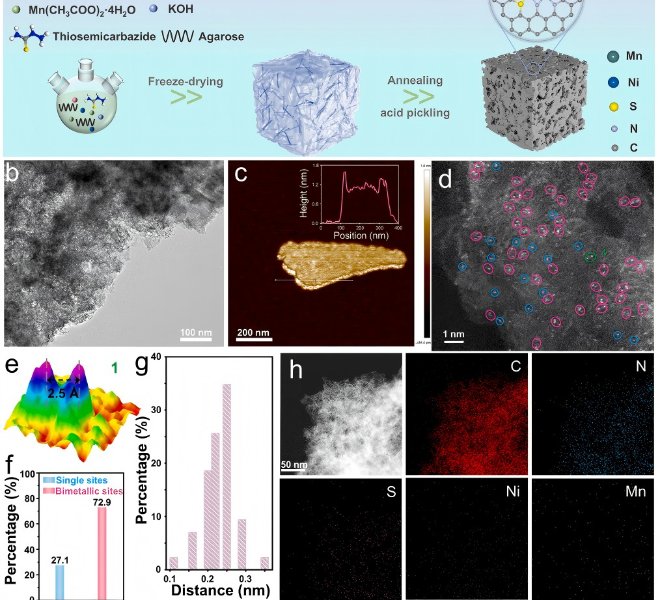
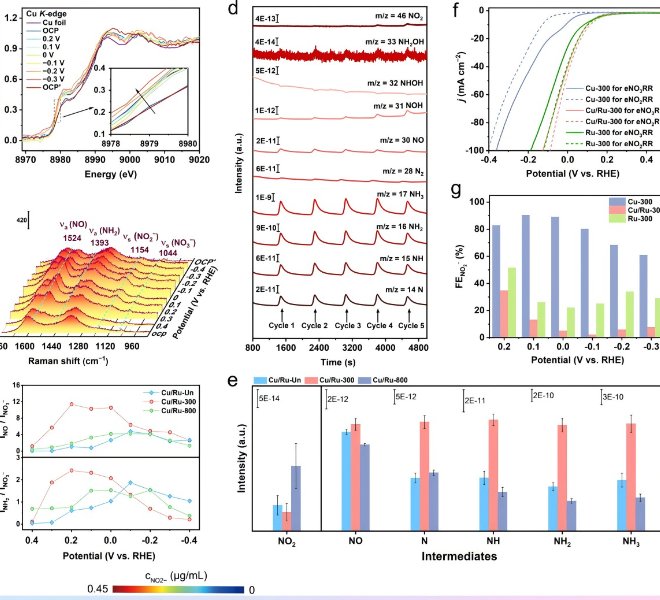
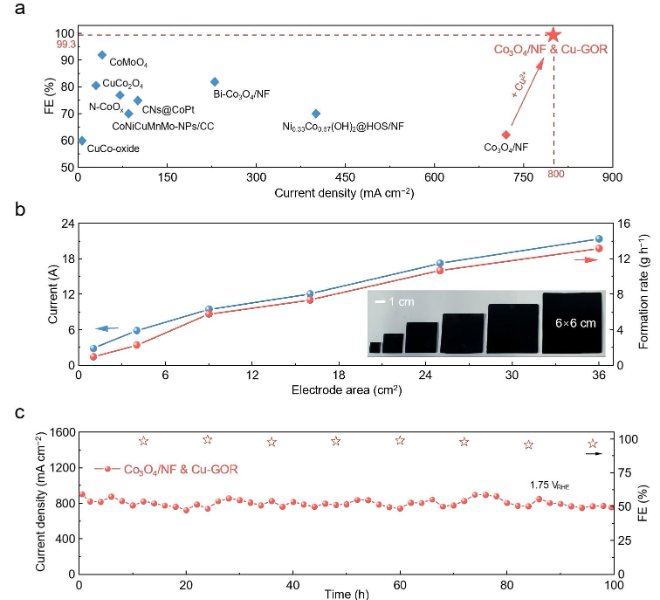
![1690183949127670.jpg 1.jpg]()
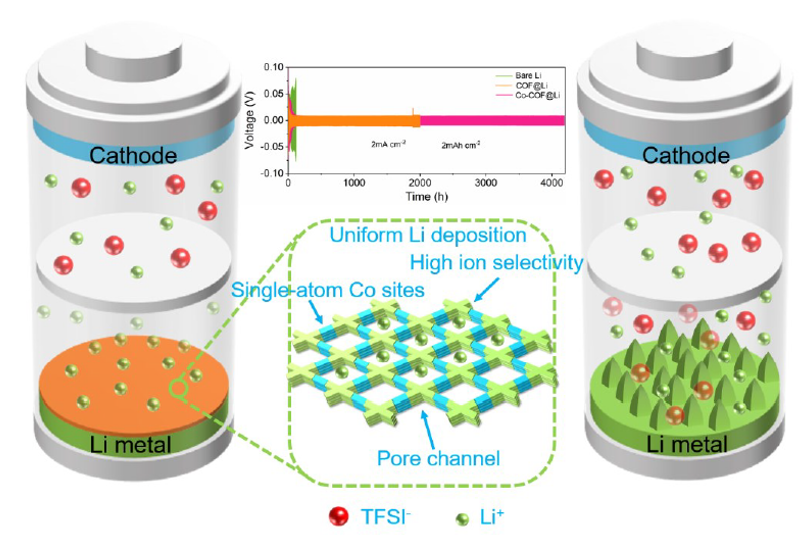
In the field of lithium batteries, lithium dendrite growth and the instability of the solid electrolyte interface (SEI) have been key issues limiting their practical application. Recently, the team of Professor Guo Hong of Yunnan University successfully confined a single cobalt atom to a covalent organic framework (sp²c-COF) and used the material as an artificial SEI film on the surface of the lithium metal anode (LMA) to regulate the interfacial stability.
In the XAFS test, the data we obtain is not necessarily smooth and has a good signal-to-noise ratio, but there will always be noise in the data due to factors such as uneven sample grinding, bubbles in situ, glitch of the light source itself, or an unreasonable piece of data, so it is necessary to use the function of noise removal or data truncation.![1690185524804591.png 640.png]()
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the mechanism of action of the material
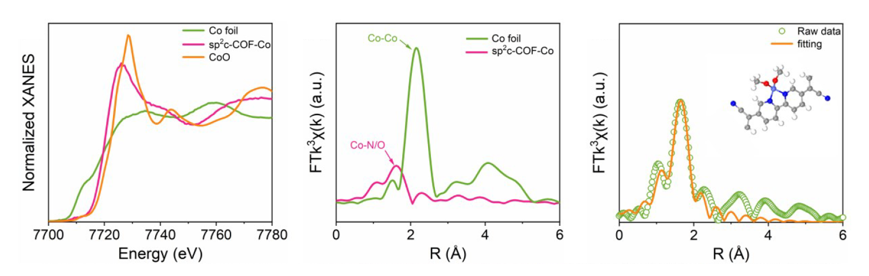
In this study, it is found that the cobalt-nitrogen coordination and strong electron-attracting cyano group in sp²c-COF-Co can effectively adjust the local electronic structure and create an electron-rich environment, thereby increasing the lithium-ion binding energy and reducing the lithium nucleation overpotential. In addition, the special pore structure of sp²c-COF-Co facilitates the rapid migration of lithium ions. Therefore, the sp²c-COF-Co-modified LMA effectively inhibited+ the formation of lithium dendrites and exhibited excellent electrochemical properties. At a current density of 2 mA cm-2, the symmetrical sp²c-COF-Co@Li battery can achieve an ultra-long cycle life (6000 hours) and the capacity retention and rate performance of the full cell are significantly improved.Notably, sp²c-COF-Co-modified Li|Cu cells exhibit satisfactory lithium utilization and operating life. The successful application of sp²c-COF-Co ASEI thin films will provide new ideas for solving the problem of lithium dendrite growth and nucleation in lithium metal batteries.Based on RapidXAFS 2M, the local structure of sp₂c-COF-Co was analyzed. As shown in Figure 2 X-ray Absorption Fine Structure Spectrum (XANES), the absorption edge position of sp²c-COF-Co is comparable to that of CoO, indicating that the cobalt atom in sp²c-COF-Co is about +2 valence. In the R-space spectrum, it was found that sp²c-COF-Co only had an obvious peak around 1.59 Å, and no Co-Co scattering peak at 2.14 Å was observed, indicating that the coordination of cobalt atoms with nitrogen (oxygen) atoms did not form metal nanoparticles or clusters. The coordination numbers of Co-N and Co-O were about 2.1 and 2.5, respectively, proving that each cobalt atom coordinated with two oxygen and two nitrogen atoms, forming the coordination structure of Co-N₂O₂. The above results suggest that the cobalt single-atom center coordinates with the bipyridine site and the methanol group via Co-N(O) bonds.![1690185542581665.png 640 (1).png]()
Fig.2 XAFS characterization and fitting results