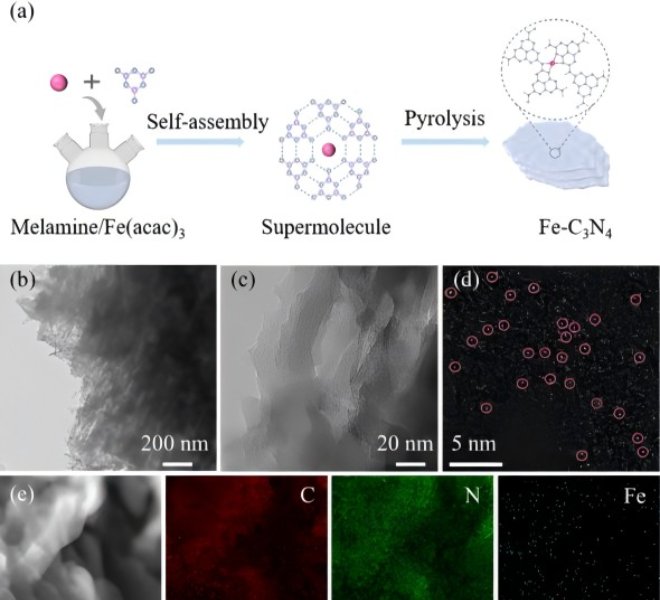
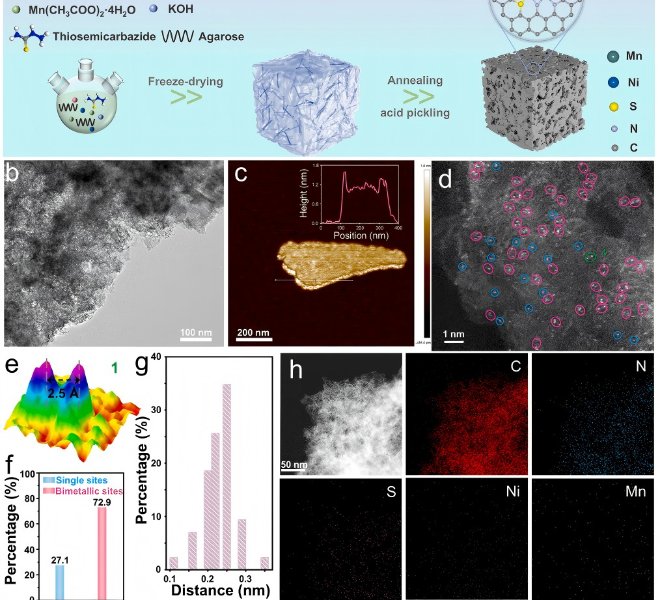
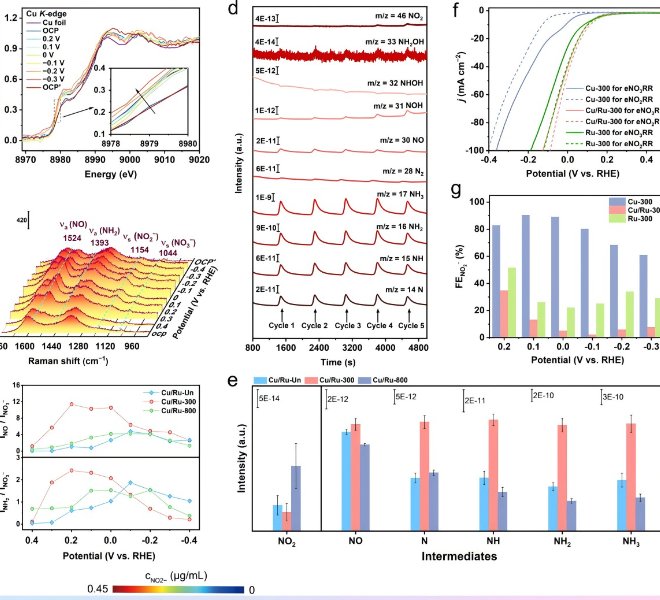
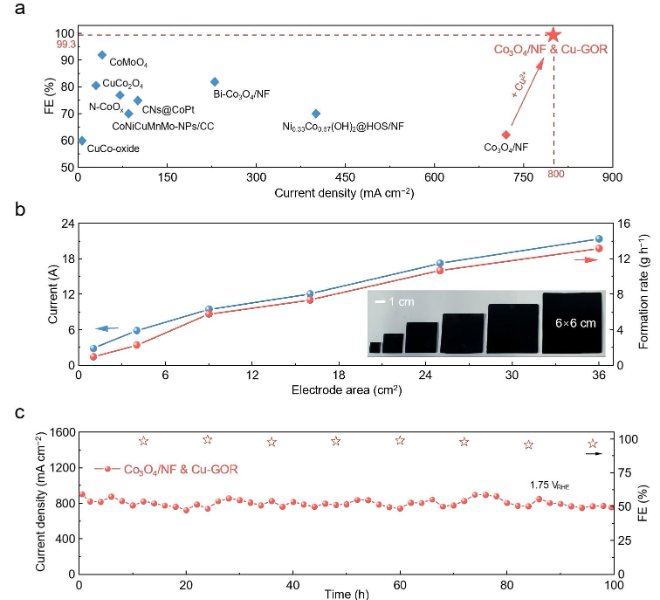
Benchtop XAFS facilitates the characterization of atomic-level dispersed active site catalysts, and the scientific research results have been published in top international journals!
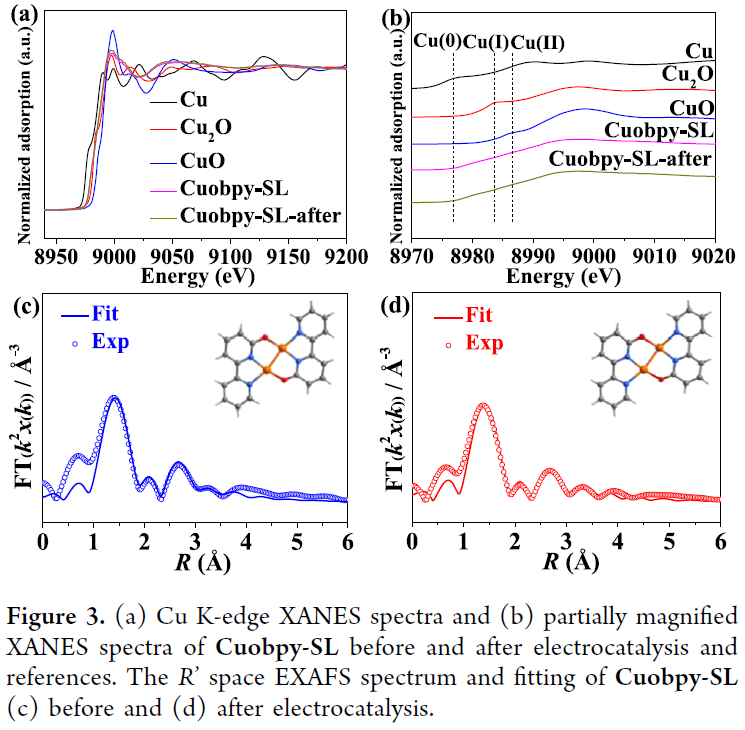
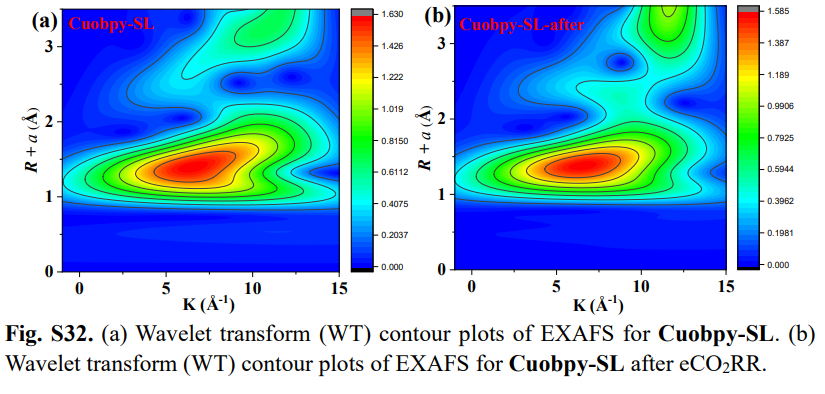
The benchtop XAFS (model: RapidXAFS 1M) facilitates the characterization of atomic-scale dispersed active site catalysts, and the scientific research results were published in the form of a paper in the top international journal J. Am. Chem. Soc.: "Dual-core copper(I) site confined to a monolayer of metal-organic layer promotes CO2 in a neutral electrolyte." Electroreduction toCH4".
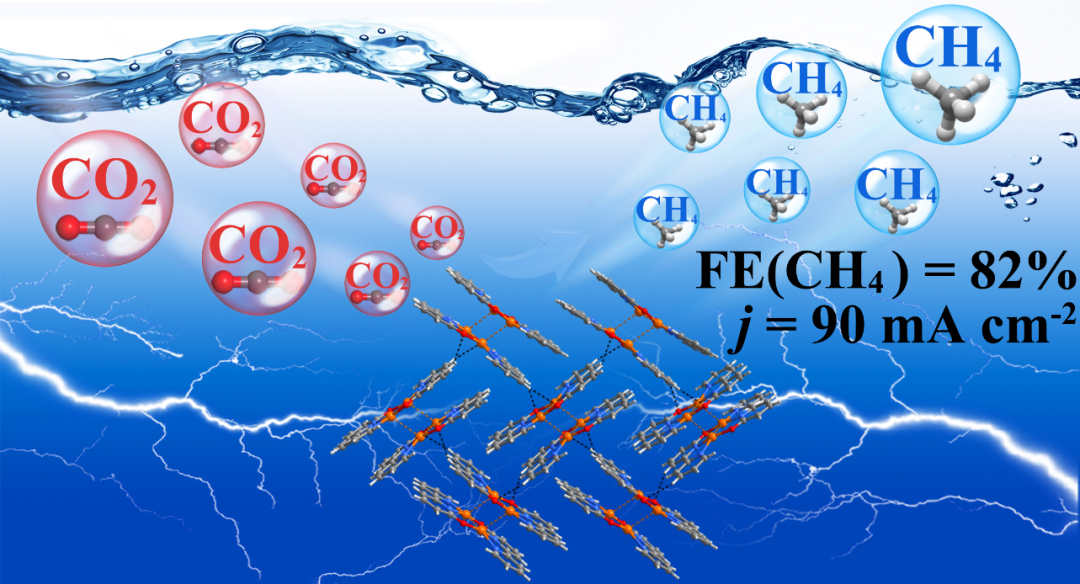
The overuse of traditional fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas has led to excessive carbon dioxide emissions, leading to a series of environmental problems that need to be solved urgently. Currently, carbon dioxide can be converted into valuable chemicals by various methods. Among them, the electrochemicalCO2 reduction reaction (eCO2RR) driven by renewable electricity provides an effective strategy to utilizeCO2 and reduceCO2 emissions. It is well known that copper-based electrocatalysts can selectively catalyze the production of hydrocarbons byeCO2RR. Although significant progress has been made ineCO2RRtoCH4, conversion usually takes place in a strong alkaline electrolyte. It is important to note that under alkaline conditions,CO2 will react with OH– to form carbonates, resulting in significantCO2 loss and increasing the likelihood of gas diffusion channel blockage. If it can achieve high-performance conversion under neutral or acidic conditions, it will be more suitable for industrialization. In fact, the current density of the methane moiety of most catalysts is less than 50 mA cm–2 under neutral conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to develop more effective catalysts and understand their mechanisms to promote the production ofCH4 byeCO2RRunder neutral conditions.

安徽吸收谱仪器设备有限公司由院士牵头,基于同步辐射背景的博士在吸收/发射谱领域10余年的技术研究积累,开发标准化的台式X射线吸收/发射谱设备。专注于X射线吸收/发射谱技术和光谱仪器开发,为科研人员提供专业的吸收/发射谱技术解决方案;秉承着“让XAFS走进实验室”的技术追求,钻研吸收/发射谱技术,发扬工匠精神和现代科学创新精神,持之以恒推进X射线技术和仪器设备研发。作为专业的XAFS人,一直做专业的XAFS设备,致力于助您XAFS自由。