RapidXAFS has successfully published several articles on the characterization of single-atom catalysts with loads as low as 0.12wt%!
Single-atom catalysts (SACs) are a hot field in the field of heterogeneous catalysis in recent years, and compared with traditional supported nanoparticle catalysts, they have attracted extensive attention due to their high efficiency and tunable active center. Spherical aberration-corrected electron microscopy (AC-TEM) and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy are indispensable for the characterization of SAC. AC-TEM can be used to visually observe the distribution of local single-atom sites, and characterize the single-atom load on the surface of the carrier. To further characterize the overall dispersion of a single atom on a support, it is necessary to understand the microstructure of the single atom, including the atomic structure and electronic structure information. XAFS is sensitive to the structural and chemical environment of the central absorbing atoms, making it the most powerful tool for studying the local structure of materials. XAFS provides information about the distance between the absorbing atom and its neighbors, the number and type of coordination atoms, the degree of disorder, and the oxidation state of the atom, all of which are parameters for determining the local geometry and electronic structure. However, for a long time, XAFS can only be tested on various synchrotron radiation light sources, which is difficult to meet the growing testing needs of scientific researchers. Adhering to the concept of bringing XAFS technology into every laboratory, Anhui Absorption Spectroscopy Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd. has launched a new desktop X-ray absorption fine structure spectrometer RaipXAFS. With extremely high sensitivity and light source quality, RaipXAFS obtains XAFS data comparable to synchrotron radiation light source XAFS, and realizes valence analysis and coordination structure analysis of elements.
Figure 1: Physical diagram of benchtop X-ray absorption fine structure spectrometer
RapidXAFS Advantages:
High performance: Provide research-grade high-quality XAFS data;
Energy range: 4.5-15 keV, expandable to 20keV;
High luminous flux: up to 2,000,000 photons/sec@8keV;
For low-concentration sample testing, C-N support can achieve 0.1wt% sample XANES test and 0.5wt% sample EXAFS test;
Benchtop design, XFAS test can be completed without synchrotron radiation light source, which can meet the daily sample analysis in the laboratory;
In-situ test (high temperature and high pressure, low temperature and low pressure, under various atmospheric conditions), in-situ observation of the reaction process;
Low maintenance cost: no need for special personnel to maintain, operate, manage, etc.
Since the establishment of the company in May 2022, RapidXAFS has sold 20 sets of equipment in domestic units, and has published 48 in the fields of battery, catalysis, and environmentin which Nat. Commun.,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,Adv. Mater.,Angew. Chem. Int. Edit.,ACS Catal.,Appl. Catal. B-Environ. More than 80% of the papers in high-grade journals and more than 70% of the articles with sample content below 5%. In this article, we will introduce the representative articles published by researchers in the field of single-atom catalysts using RapidXAFS:
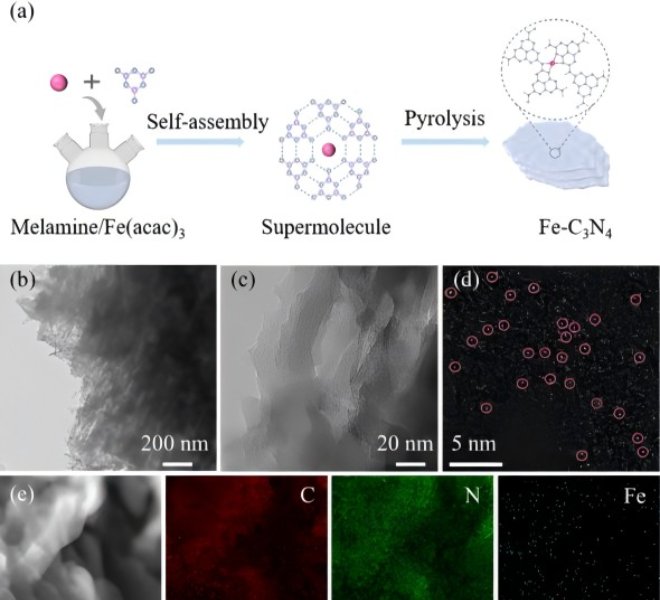
Article 1 (Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 123509) Load as low as 0.12wt%: Enhanced full-pH oxygen reduction by the modulation of electron spin states and the construction of diatomic tandem reactions
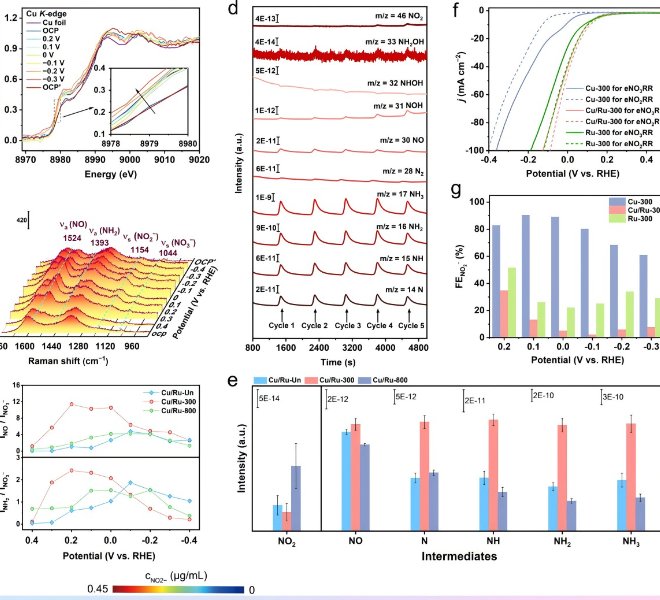
The phenomenal growth of carbon dioxide has created an urgent need for clean energy technologies. Zinc-air batteries are a promising clean and sustainable energy conversion device, and their slow oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) on the air cathode requires efficient catalysts to improve the reaction kinetics. However, the binding energy of closely related ORR intermediates at a single catalytic site cannot be adjusted independently due to the insurmountable proportional relationship, which becomes a bottleneck to further improve their kinetics. Therefore, how to solve this pain point is the current research hotspot. Recently, the team of Professor Guo Hong of Yunnan University has been working in Appl. Catal. B: Environ.In a paper entitled "Modulation of electronic spin state and construction of dual-atomic tandem reaction for enhanced pH-universal oxygen reduction", an atomically dispersed Fe,Cu/ The N-C catalyst, combined with the advantages of electron spin state modulation and tandem reaction mechanism, exhibits excellent ORR performance over a wide pH range. The authors used a benchtop XAFS (model RapidXAFS 1M) from Anhui Absorption Spectroscopy Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd. to complete the structural characterization of Fe, Cu/N-C catalysts, where the K side of Fe at 1.5Å and the K side of Cu at 1.41Å are Fe-N and Cu-N bonds, respectively, which proves that Fe and Cu are single-atom dispersed. Combined with theoretical calculations, it is proved that the improvement of ORR performance is due to the spin state transition of the metal site and the fast four-electron tandem reaction, which jointly promotes the thermodynamics and kinetics of *O2 adsorption and *OH desorption. Furthermore, Fe,Cu/N-C was used to assemble liquid zinc-air batteries (ZABs), which made the ZABs have good peak power density and open-circuit voltage (OCV), which were superior to commercial Pt/C-driven batteries, and could still present stable charge-discharge curves under characteristic deformations such as bending, twisting, folding and cutting. Therefore, Fe, Cu/N-C has great application potential in the field of flexible wearable electronics.
Fig.2 XAFS spectra of Fe, Cu/N-C and Cu
Article 2 (J. Am. Chem. Soc., 3c08571) confined to a monolayer of metal-organic layers promotes the electroreduction of CO2 to CH4 in a neutral electrolyte
The overuse of traditional fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas has led to excessive carbon dioxide emissions, leading to a series of environmental problems that need to be solved urgently. An electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (eCO2RR) powered by renewable electricity provides an effective strategy for utilizing CO2 and reducing CO2 emissions. Normally eCO2RR to CH4 is carried out in a strong alkaline electrolyte, but under alkaline conditions, CO2 will react with OH– to form carbonates, resulting in significant CO2 loss and increasing the likelihood of gas diffusion channel blockage. Therefore, the development of catalysts that can achieve high-performance conversion under neutral or acidic conditions will have great application potential. Recently, Professor Liao Peiqin's team from Sun Yat-sen University has been working at J. Am. Chem. SocIn a paper entitled "Dicopper(I) Sites Confined in a Single Metal–Organic Layer Boosting the Electroreduction of CO2 to CH4 in a Neutral Electrolyte", the paper analyzes the efficient production of CH in a neutral aqueous solution by monolayer metal-organic layer nanosheets under the action of double copper(I) active sites4and no significant performance degradation for 100 hours of continuous operation. The authors used a benchtop XAFS (model RapidXAFS 1M) from Anhui Absorption Spectroscopy Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd. to characterize the structure of Cuobpy-SL before and after electrolysis at only 1.4 The characteristic peak near Å was observed, and the Cu-Cu scattering peak at 2.3Å was not observed, indicating that the Cu atoms in Cuobpy-SL were mainly coordinated with oxygen before and after electrolysis, and there were no large metal clusters or particles, and the stability of Cuobpy-SL was demonstrated.
Fig.3 XAFS spectra of Cu before and after Cuobpy-SL electrolysis
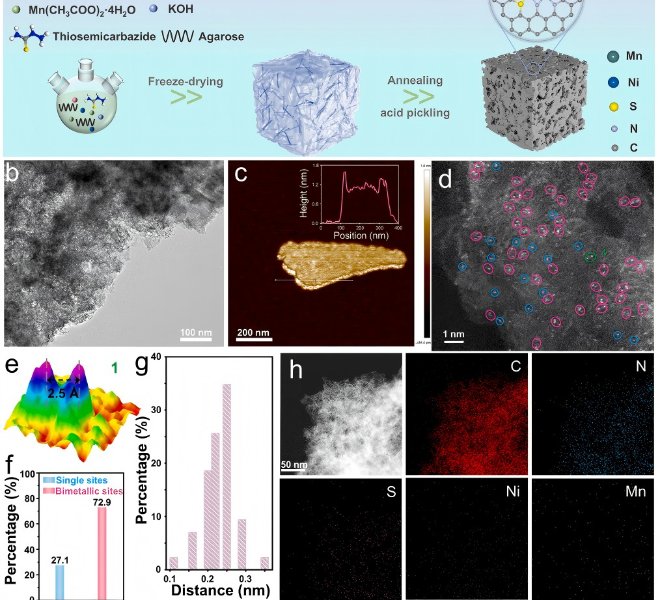
Article 3 (Adv. Mater., 202304511) Single-atom Co-site COF design to control the local coordination environment of lithium ions to realize dendritic lithium metal batteries
Lithium metal has a high theoretical specific capacity (3860mAHg-1) and a low electrochemical potential (3.04Vvs SHE), which is an ideal anode material for future lithium metal batteries (LMB). Unfortunately, lithium metal anodes (LMAs) face serious Li dendrite problems due to the uneven deposition behavior of lithium. Recently, the team of Professor Guo Hong of Yunnan University held a conference in Adv. Mater.He has published a paper entitled "Regulating the Lithium Ions' Local Coordination Environment through Designing COF with Single Atomic Co Site to Achieve Dendrite-Free Llithium Metal Batteries". An atomically dispersed cobalt coordination bipyridine-rich covalent organic framework (sp2c-COF-Co) was designed as artificial SEI on the surface of lithium metal anode to solve these problems. The authors used a benchtop XAFS (model RapidXAFS 2M) from Anhui Absorption Spectroscopy Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd. to analyze the local structure of sp2c-COF-Co and found that sp2c-COF-Co Only a significant peak was observed around 1.59 Å, and no Co-Co scattering peak at 2.14 Å was observed, indicating that the coordination of cobalt atoms with nitrogen (oxygen) atoms did not form metal nanoparticles or clusters. And by fitting, it was demonstrated that the cobalt single-atom center was coordinated with the bipyridine site and the methanol group by Co-N(O) bonding. Under the joint action of Co-N coordination and cyano group, a large number of charges were transferred to sp2 c-COF, which enhanced the adsorption of Li+ by sp2c-COF. Sp2c-COF-Co modified cells have excellent electrochemical properties at ultra-high current densities (2 mA cm-2), Li|The Li symmetrical battery can be stable for more than 6000 hours. This strategy has potential value for inhibiting the formation of Li dendrite and promoting the development of COF artificial solid electrolyte interfacial phase.
Fig. 4 XAFS spectra of Co of sp²c-COF-Co
Article 4 (J. Am. Chem. Soc., 3c06665) Molecular Spacer Optimization of Spatial Density of Single-Atom Co Loci Promotes Sustainable Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation
The study of single-atom catalysts (SACs) provides a new solution for the design and synthesis of high-efficiency electrocatalysts with high activity and plateau utilization. One of the common strategies used to improve SAC performance is to increase the loading of metal atoms. However, as the metal loading increases, the agglomeration of metals or active centers is unavoidable, which will limit the further increase in the effective active density (or actual atom utilization) of the catalyst. Recently, the team of Professor He Chunting of Jiangxi Normal University was in J. Am. Chem. SocPublished in "Optimizing Spatial Density of Single Co Sites via Molecular Spacing for Facilitating Sustainable Water Oxidation" In this paper, a series of different organic anhydrides were used as spacer molecules to regulate the spatial density of a single Co site in discrete metal phthalocyanine, and a new type of molecular-based single-atom catalysts (msSACs) were designed and synthesized, which significantly improved the effective active site density and mass transfer performance, thereby changing the apparent activation energy of the catalysts. In this work, the authors used a benchtop XAFS (model RapidXAFS 1M) from Anhui Absorption Spectroscopy Instrument Equipment Co., LtdThe characterization of three different organic anhydrides as spacer molecules did not significantly change the electronic structure and coordination environment of Co, confirming that the spacer density of single-atom sites was mainly optimized by the molecular spacer strategy. On the other hand, XAFS spectroscopy also confirmed that the coordination environment of CoPc-PM@CNT remained unchanged before and after the OER reaction, which corroborated the excellent long-term stability test results of such msSACs. This work provides a molecular spacing strategy to optimize the spatial density of single-atom sites, providing a new perspective for designing cost-effective electrocatalysts for sustainable industrial applications.
图5 左:三种分子间隔单原子催化剂中Co的XAFS谱;右:CoPc-PM@CNT OER反应前后Co的XAFS谱和小波变换
Article 5 (Adv. Mater., 202209644) Single-atom iron site electronic structure engineering for improving zinc-air battery performance
The development of advanced energy conversion and storage technologies is essential to achieve the goal of alleviating the energy crisis with clean energy. In terms of renewable energy systems, rechargeable metal-air batteries and proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) have attracted extensive attention due to their high energy density, low cost, and environmental protection. The efficiency of electrocatalysts is highly dependent on the electrochemical reactions associated with oxygen, including oxygen reduction (ORR) and oxygen evolution (OER). However, the poor activity and slow kinetics of the four-proton-coupled electron transfer step in ORR and OER seriously hinder their application in zinc-air batteries. Recently, Li Zhijun's team from Northeast Petroleum University and He Cheng's team from Xi'an Jiaotong University have been working in Adv. Mater.In a paper entitled "Engineering the Electronic Structure of Single Atom Iron Sites with Boosted Oxygen Bifunctional Activity for Zinc-Air Batteries", a strategy for the preparation of catalysts consisting of atomically dispersed iron atoms supported by mesoporous nitrogen-doped carbon supports ( Fe SAs/NC). The authors used the desktop XAFS (model RapidXAFS 2M) of Anhui Absorption Spectroscopy Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd. to characterize the local structure, in Fe SAs/NC with positive charge, the valence state is between +2 and +3, and the Fe SACs/NC is 1.78 There is a main peak at Å, which is close to the peak of the reference FePc, and there are no coordination peaks for Fe-O and Fe-O-Fe, so Fe in the catalyst is atomically dispersed. The authors further investigated the atomic dispersion and coordination environment of Fe in the Fe1/NC reference sample, and the results showed that these isolated Fe atoms were positively charged in the Fe1-N4 coordination environment. In the full pH range, Fe SAs/NC exhibited good catalytic activity for ORR reactions, and Fe SAs/NC exhibited a low overpotential of 320 mV (10 mA cm-2) in the alkaline OER reactionconditions). The catalyst is assembled into a zinc-air battery, which is far superior to Pt/C+RuO2 in terms of power density, specific capacity, and cycle stability. Theoretical calculations show that the charge distribution and electron-metal-support interaction of Fe can be effectively optimized by regulating the local coordination environment of the Fe site, which can affect the adsorption and activation of oxygen-containing intermediates at the Fe site. This work shows that the regulation of the local electronic structure of the active site is of great significance in improving the activation of small molecules by electrocatalysts.
Fig.6 XAFS spectra of Fefor Fe 1/NC
Some of the articles have been published
1. Zhang, Z. et al (2024). Nat Commun, 15, 391.
2. Liao P., et al (2024). J Am Chem Soc, 3c12423.
3. Guo, H., et al (2023). Adv Mater, 202304511.
4. Zhu. J., et. al (2023). Adv Mater, 202209644.
5. Chen, X. et al (2023). J Am Chem Soc, 3c08571.
6. He, C. et al (2023). J Am Chem Soc, 3c06665.
7. Zheng, L. et al (2023). J Am Chem Soc, 3c05552.
8.Luo, W. et, al. (2023). Angew Chem Int Ed. e202216835. (First in situ OER reaction XAS article).
9.Yang, J. et, al. (2023). Angew Chem Int Ed. e202315834.
10.Wang, X. et, al. (2023). Angew Chem Int Ed. 202313886.
11.Li, L., et al (2023). Angew Chem Int Ed, e202307160.
12.Xu Y., et al. (2023). Angew Chem Int Ed, e202317664.
13. Wu H., et, al. (2023). Small, 2307637. (First article on in-situ CO2RR reactions).
Contact us
Anhui Absorption Spectrum Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd. is led by experts, based on the background of synchrotron radiation in the field of absorption/emission spectrum of more than 10 years of technical research accumulation, the development of standardized desktop X-ray absorption/emission spectrum equipment. Focusing on the development of X-ray absorption/emission spectrum technology and spectroscopy instruments, providing professional absorption/emission spectrum technology solutions for scientific researchers, adhering to the technical pursuit of "bringing XAFS into the laboratory", delving into absorption/emission spectrum technology, carrying forward the spirit of craftsmanship and modern scientific innovation, and persistently promoting the research and development of X-ray technology and equipment. As a professional XAFS person, we have been making professional XAFS equipment and are committed to helping you XAFS freedom.